on video How does a Transformer work ?
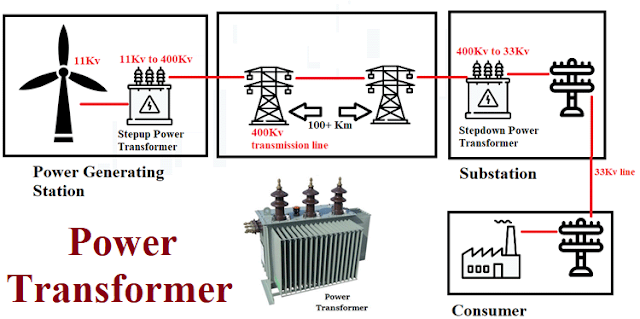
Transformers are electrical devices consisting of two or more coils of wire that are used to transfer electrical energy by means of a magnetic field. Transformers are very simple static electro-magnetic passive electrical devices that work on the principle of Faraday's law of induction by converting electrical energy from one value to another. The two electrical circuits are linked through mutual induction, which is the process by which a coil of wire magnetically induces a voltage into another coil that is located in close proximity. Electrical energy passes more efficiently from one coil to the other by wrapping the coils around a core. The voltage and current levels are either increased or decreased, without modifying the frequency. Higher AC transmission voltages and currents can be reduced to a much lower, safer, and usable voltage level where it can be used to supply electrical equipment in homes and workplaces.
A single-phase voltage transformer consists of two electrical coils of wire, the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding takes power, while secondary winding delivers power. The two coils are not electrically connected, but rather linked magnetically. If the second coil has the same number of turns as the first coil, the electric current in the second coil will be virtually the same size as the one in the first coil. A step-down transformer is when the first coil (primary winding) has more turns than the second coil (secondary winding), so the secondary voltage is smaller than the primary voltage. A step-up transformer is when the first coil has less turns than the second coil, causing the secondary voltage to be higher than the primary voltage.
As mentioned earlier, the coils are wrapped around a core. The core can be made of a few different materials. First is the iron core transformer, which uses soft iron plates as the core material. The iron has excellent magnetic properties, causing the flux linkage of the iron core transformer to be high, so the efficiency is also high. A ferrite core transformer uses a ferrite core, which has high magnetic permeability and offers very low losses in the high-frequency applications. Often ferrite core transformers are used in switch mode power supplies or RF related applications. Toroidal core transformer uses toroid-shaped core material (ring or donut shaped), such as iron core or ferrite core. The ring shape makes the leakage inductance very low. In an air core transformer, the flux linkage is made entirely using the air; however, they produce low mutual inductance compared to a transformer with a physical core.
Your may also be interested in reading: What is Alternating Current
En savoir plus sur ce texte sourceVous devez indiquer le texte source pour obtenir des informations supplémentaires
Transformers are electrical devices consisting of two or more coils of wire that are used to transfer electrical energy by means of a magnetic field. Transformers are very simple static electro-magnetic passive electrical devices that work on the principle of Faraday's law of induction by converting electrical energy from one value to another. The two electrical circuits are linked through mutual induction, which is the process by which a coil of wire magnetically induces a voltage into another coil that is located in close proximity. Electrical energy passes more efficiently from one coil to the other by wrapping the coils around a core. The voltage and current levels are either increased or decreased, without modifying the frequency. Higher AC transmission voltages and currents can be reduced to a much lower, safer, and usable voltage level where it can be used to supply electrical equipment in homes and workplaces.
A single-phase voltage transformer consists of two electrical coils of wire, the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding takes power, while secondary winding delivers power. The two coils are not electrically connected, but rather linked magnetically. If the second coil has the same number of turns as the first coil, the electric current in the second coil will be virtually the same size as the one in the first coil. A step-down transformer is when the first coil (primary winding) has more turns than the second coil (secondary winding), so the secondary voltage is smaller than the primary voltage. A step-up transformer is when the first coil has less turns than the second coil, causing the secondary voltage to be higher than the primary voltage.
As mentioned earlier, the coils are wrapped around a core. The core can be made of a few different materials. First is the iron core transformer, which uses soft iron plates as the core material. The iron has excellent magnetic properties, causing the flux linkage of the iron core transformer to be high, so the efficiency is also high. A ferrite core transformer uses a ferrite core, which has high magnetic permeability and offers very low losses in the high-frequency applications. Often ferrite core transformers are used in switch mode power supplies or RF related applications. Toroidal core transformer uses toroid-shaped core material (ring or donut shaped), such as iron core or ferrite core. The ring shape makes the leakage inductance very low. In an air core transformer, the flux linkage is made entirely using the air; however, they produce low mutual inductance compared to a transformer with a physical core.
Your may also be interested in reading: What is Alternating Current
En savoir plus sur ce texte sourceVous devez indiquer le texte source pour obtenir des informations supplémentaires





![Transformateurs triphasés [ l'étoile - triangle]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgfrGJWOWiKdh5DvfZk3WZSqBi10gXs2khB0NJtJhI44hX7zjU1gkqKTpeTDbpmMEzgZXpfdzdyIDt6xOo7P1bZbYfm5_Jb4LQ8TZFzybV_heL92b5TI7yk1noqyINhckwGqU4dR70A8sDd/s72-c/triangle-etoile.png)
No comments